Model-View-Controller
- Architectural
Intent
Separate the user interface into three interconnected components: the model, the view and the controller. Let the model manage the data, the view display the data and the controller mediate updating the data and redrawing the display.
Explanation
Real-world example
Consider ICU room in hospital which displays the patients health information on device displays which are taking input from sensors connected to patient. Here, display's job is to display the data that it receives from the controller which in turn gets update from sensor model.
In plain words
MVC separates the business logic from user interface by mediating Controller between Model & View.
Wikipedia says
Model–view–controller (MVC) is commonly used for developing user interfaces that divide the related program logic into three interconnected elements. This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to and accepted from the user.
Programmatic Example
Consider following GiantModel model class that provides the health, fatigue & nourishment information.
public class GiantModel {
private Health health;
private Fatigue fatigue;
private Nourishment nourishment;
/**
* Instantiates a new GiantModel.
*/
public GiantModel(Health health, Fatigue fatigue, Nourishment nourishment) {
this.health = health;
this.fatigue = fatigue;
this.nourishment = nourishment;
}
public Health getHealth() {
return health;
}
public void setHealth(Health health) {
this.health = health;
}
public Fatigue getFatigue() {
return fatigue;
}
public void setFatigue(Fatigue fatigue) {
this.fatigue = fatigue;
}
public Nourishment getNourishment() {
return nourishment;
}
public void setNourishment(Nourishment nourishment) {
this.nourishment = nourishment;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("The giant looks %s, %s and %s.", health, fatigue, nourishment);
}
}
GiantView class to display received patient data.
public class GiantView {
public void displayGiant(GiantModel giant) {
LOGGER.info(giant.toString());
}
}
And GiantController class that takes updates from GiantModel & sends to GiantView for display.
public class GiantController {
private final GiantModel giant;
private final GiantView view;
public GiantController(GiantModel giant, GiantView view) {
this.giant = giant;
this.view = view;
}
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedReturnValue")
public Health getHealth() {
return giant.getHealth();
}
public void setHealth(Health health) {
this.giant.setHealth(health);
}
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedReturnValue")
public Fatigue getFatigue() {
return giant.getFatigue();
}
public void setFatigue(Fatigue fatigue) {
this.giant.setFatigue(fatigue);
}
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedReturnValue")
public Nourishment getNourishment() {
return giant.getNourishment();
}
public void setNourishment(Nourishment nourishment) {
this.giant.setNourishment(nourishment);
}
public void updateView() {
this.view.displayGiant(giant);
}
}
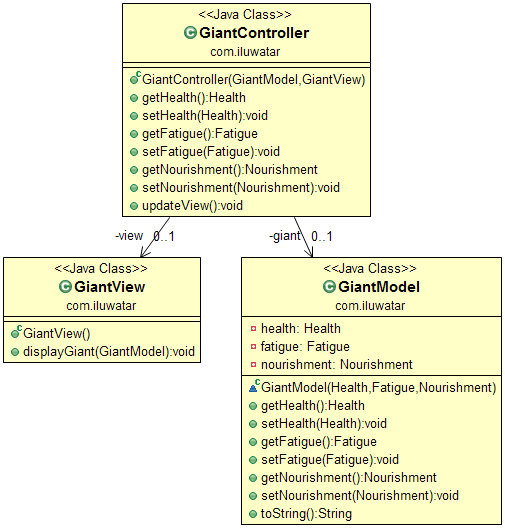
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Model-View-Controller pattern when
- You want to clearly separate the domain data from its user interface representation