Static Content Hosting
- Cloud
Intent
Deploy static content to a cloud-based storage service that can deliver them directly to the client. This can reduce the need for potentially expensive compute instances.
Explanation
Real world example
A global marketing web site with static content needs to be quickly deployed to start attracting potential customers. To keep the hosting expenses and maintenance minimum, a cloud hosted storage service along with content delivery network is used.
In plain words
Static Content Hosting pattern utilizes cloud native storage service to store the content and global content delivery network to cache it in multiple data centers around the world.
On a static website, individual webpages include static content. They might also contain client-side scripts such as Javascript. By contrast, a dynamic website relies on server-side processing, including server-side scripts such as PHP, JSP, or ASP.NET.
Wikipedia says
A static web page (sometimes called a flat page or a stationary page) is a web page that is delivered to the user's web browser exactly as stored, in contrast to dynamic web pages which are generated by a web application.
Static web pages are suitable for content that never or rarely needs to be updated, though modern web template systems are changing this. Maintaining large numbers of static pages as files can be impractical without automated tools, such as static site generators.
Example
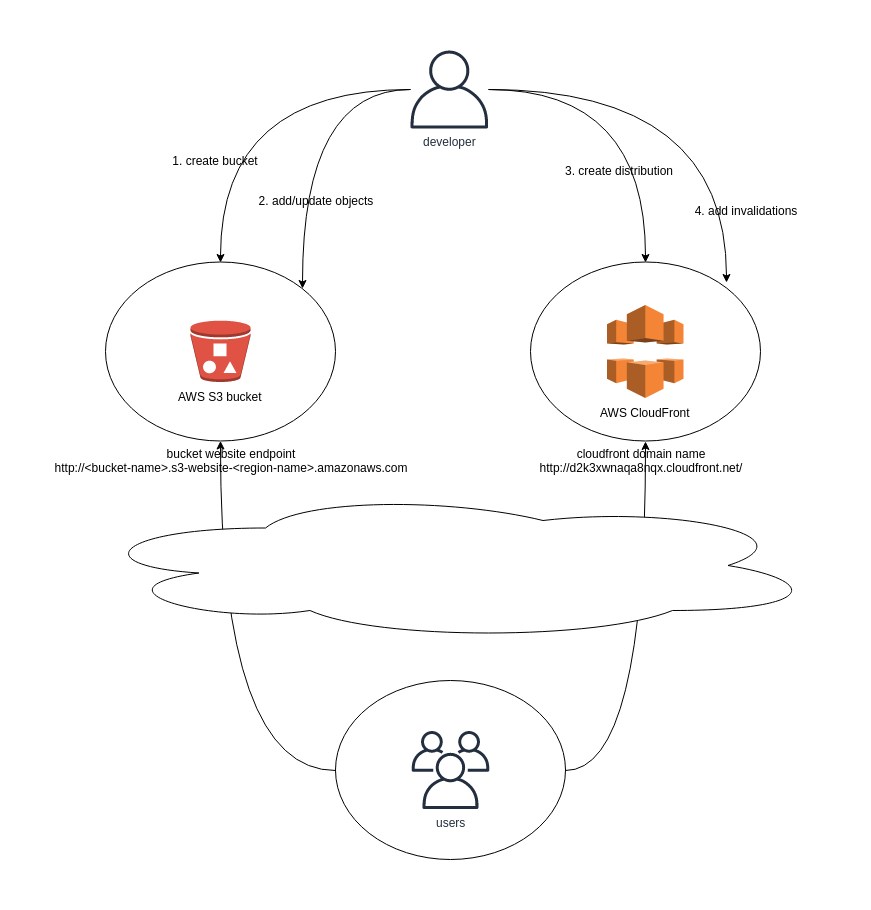
In this example we create a static web site using AWS S3 and utilize AWS Cloudfront to distribute the content globally.
First you will need an AWS account. You can create a free one here: AWS Free Tier
Login to the AWS Console
Go to Identity and Access Management (IAM) service.
Create IAM user that has only the necessary rights for this application.
- Click
Users - Click
Add user. ChooseUser nameas you wish andAccess typeshould beProgrammatic access. ClickNext: Permissions. - Choose
Attach existing policies directly. SelectAmazonS3FullAccessandCloudFrontFullAccess. ClickNext: Tags. - No tags are necessarily needed, so just click
Next: Review. - Review the presented information and if all seems good click
Create user. - You are presented with
Access key IDandSecret access keywhich you will need to complete this example, so store them safely. - Click
Close.
- Click
Install AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) to gain programmic access to AWS cloud.
Configure AWS CLI with command
aws configureas desribed in the instructionsCreate AWS S3 bucket for the web site content. Note that the S3 bucket names must be globally unique.
- The syntax is
aws s3 mb <bucket name>as described in the instructions - For example
aws s3 mb s3://my-static-website-jh34jsjmg - Verify that the bucket was successfully created with command
aws s3 lswhich list the existing buckets
- The syntax is
Configure the bucket as a web site with command
aws s3 websiteas described in the instructions.- E.g.
aws s3 website s3://my-static-website-jh34jsjmg --index-document index.html --error-document error.html
- E.g.
Upload content to the bucket.
- First create the content, at least
index.htmlanderror.htmldocuments. - Upload the content to your bucket as described here
- E.g.
aws s3 cp index.html s3://my-static-website-jh34jsjmgandaws s3 cp error.html s3://my-static-website-jh34jsjmg
- First create the content, at least
Next we need to set the bucket policy to allow read access.
- Create
policy.jsonwith the following contents (note that you need to replace the bucket name with your own).
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "PublicReadGetObject", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": "*", "Action": "s3:GetObject", "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-static-website-jh34jsjmg/*" } ] }- Set the bucket policy according to these instructions
- E.g.
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket my-static-website-jh34jsjmg --policy file://policy.json
- Create
Test the web site in your browser.
- The web site URL format is
http://<bucket-name>.s3-website-<region-name>.amazonaws.com - E.g. this web site was created in
eu-west-1region with namemy-static-website-jh34jsjmgso it can be accessed via urlhttp://my-static-website-jh34jsjmg.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com
- The web site URL format is
Create CloudFormation distribution for the web site.
- The syntax is described in this reference
- E.g. the easiest way is to call
aws cloudfront create-distribution --origin-domain-name my-static-website-jh34jsjmg.s3.amazonaws.com --default-root-object index.html - There's also JSON syntax e.g.
--distribution-config file://dist-config.jsonto pass distribution configuration arguments in file - The output of the call will show you the exact distribution settings including the generated CloudFront domain name you can use for testing e.g.
d2k3xwnaqa8nqx.cloudfront.net - CloudFormation distribution deployment takes some time, but once it's completed your web site is served from data centers all around the globe!
That's it! You have implemented a static web site with content distribution network serving it lightning fast all around the world.
- To update the web site you need to update the objects in S3 bucket and invalidate the objects in the CloudFront distribution
- To do it from AWS CLI see this reference
- Some further development you might want to do is serve the content over https and add a domain name for your site
Applicability
Use the Static Content Hosting pattern when you want to:
- Minimize the hosting cost for websites and applications that contain some static resources.
- Build a globally available web site with static content
- Monitor the web site traffic, bandwidth usage, costs etc.
Typical Use Case
- Web sites with global reach
- Content produced by static web site generators
- Web sites with no dynamic content requirements